- OSI means Open System Interconnect model.
- Developed by the International Organization for Standardization in 1984.
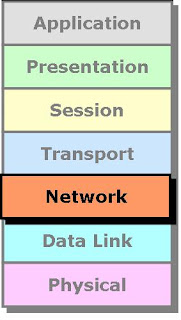
- It consists of seven layers.
- Each layer has a different but specific processing function.
OSI Model Layers
Application Layer
Application Layer is responsible for providing Networking Services to user. It also known as Desktop Layer. Identification of Services is done using Port Numbers.
Ports are nothing but Socket i.e. Entry and Exit Point to the Layer
Total No. Ports 0 – 65535
Reserved Ports 0 – 1023
Open Ports 1024 – 65535
Examples of Networking Services
Service Port No.
HTTP 80
FTP 21
SMTP 25
TELNET 23
TFTP 69
How data flows from Application Layer
Presentation Layer
Presentation Layer is responsible for converting data into standard format.
Examples : ASCII, EBCDIC, JPEG, MPEG, BMP, MIDI, WAV, MP3
Following tasks are perform at Presentation layer :
Encoding – Decoding
Encryption – Decryption
Compression – Decompression
How data flows from Presentation Layer
Session Layer
Session Layer is responsible establishing, maintaining and terminating session.
Session ID also works at Session Layer.
Examples :
RPC Remote Procedure Call
SQL Structured Query language
NFS Network File System
How data flows from Session Layer
Transport Layer
Transport Layer is responsible for end-to-end connectivity. It is also known as heart of OSI Layers. Following task are performed at Transport Layer : -
- Identifying Service
- Multiplexing & De-multiplexing
- Segmentation
- Sequencing & Reassembling
- Flow Control
- Error Correction
Identifying Service
Multiplexing & De-multiplexing
Segmentation
Sequencing & Reassembling
Sequencing & Reassembling
Error Correction
Flow Control - Windowing
How data flows from Transport Layer
Network Layer
Network Layer is responsible for providing best path to data to reach destination. Logical Addressing sits on this layer. Device working on Network Layer is Router.
It is divided into two parts
Routed Protocols
e.g. IP, IPX, Apple Talk.
Routing Protocols
e.g. RIP, IGRP, OSPF, EIGRP
Routed Protocols
Routing Protocols
How data flows from Network Layer
Datalink Layer
Datalink Layer is divided into two Sub Layers :
LLC – Logical Link Control
It talks about Wan protocols e.g. PPP, HDLC, Frame-relay
MAC – Media Access Control
It talks about Physical Address. It is 48 bit Addressing i.e. 12 digit Hexadecimal No. It is also responsible for Error Detection
Device working on Data Link Layer is Switch, Bridge, NIC.
Error Detection – CRC Check
Error Detection – CRC Check
How data flows from Data Link Layer
Physical Layer
Physical Layer is responsible for electrical, mechanical or procedural checks. Data will be converted in Binary that is 0’s & 1’s. Data will be in the form of electrical pulses if it is Coaxial or Twisted Pair cable and in the form of Light if it is Fiber Optic Cable.
Devices working at Physical Layer are Hubs, Repeaters, Cables, Modems etc.
Physical Layer Example
How data flows from Physical Layer
Data Encapsulation & De-capsulation
Comparing OSI with TCP/IP Layers



























0 comments:
Post a Comment